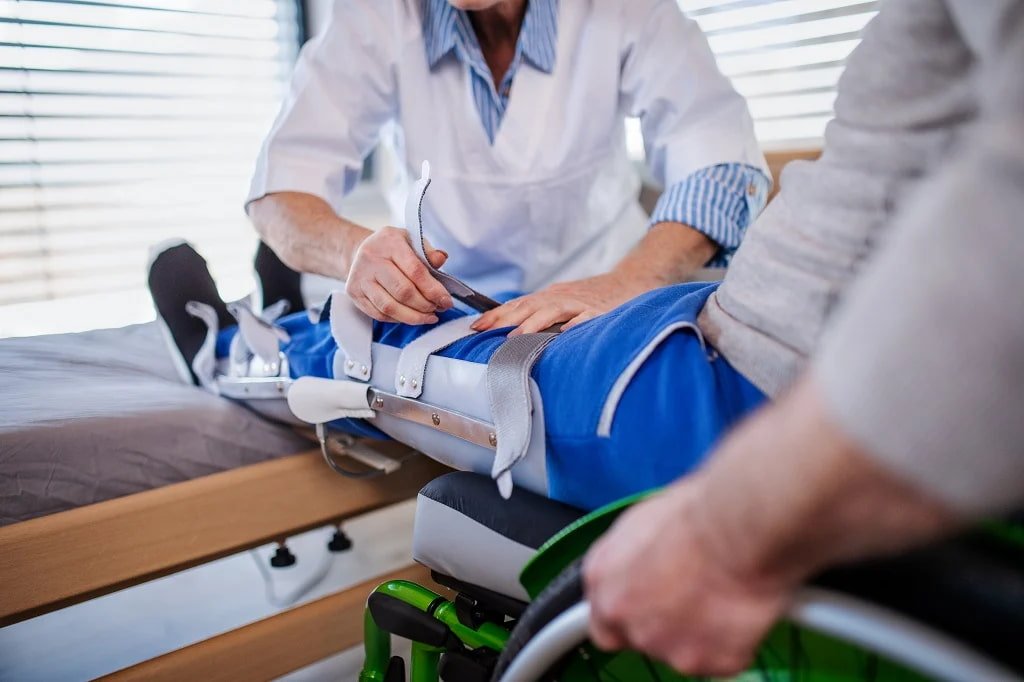
Prosthetics and orthotics are both essential fields within the medical and rehabilitation sectors, focusing on supporting and improving physical movement. While both are aimed at enhancing the mobility and quality of life for individuals, they serve different purposes. Understanding the distinction between prosthetics and orthotics is crucial for patients, healthcare professionals, and caregivers.
What Are Prosthetics?
At Hinaricare Prosthetic Clinic we involve in design, creation, and fitting of artificial limbs or body parts to replace those that are missing or amputated. They are primarily used by individuals who have lost a limb due to injury, illness, or congenital conditions. Prosthetics are custom-made for each individual to closely mimic the function and appearance of the missing body part.
Types of Prosthetics:
- Upper Limb Prosthetics: Replace arms, hands, or fingers.
- Lower Limb Prosthetics: Replace legs, feet, or toes.
- Cosmetic Prosthetics: Focus on appearance rather than function.
- Bionic Prosthetics: Advanced, robotic limbs that use muscle signals or brainwaves for precise control.
Main Purpose: Prosthetics are used to restore lost function, mobility, and aesthetic appearance after an amputation or congenital limb deficiency.
What Are Orthotics?
Orthotics involve the design and fabrication of supportive devices that are applied externally to correct or enhance the function of a body part. These devices are often used to support weakened muscles, align joints, or correct physical deformities. Unlike prosthetics, orthotics do not replace body parts but aid in improving the function of existing ones.
Types of Orthotics:
- Spinal Orthotics: Support and stabilize the spine in cases of scoliosis or spinal injuries.
- Lower Limb Orthotics: Include braces for ankles, knees, or feet to help individuals with joint or muscle issues.
- Upper Limb Orthotics: Provide support to arms or wrists, often used for conditions like carpal tunnel syndrome or after an injury.
- Foot Orthotics (Insoles): Custom shoe inserts designed to improve foot alignment and relieve pain in individuals with conditions such as flat feet or plantar fasciitis.
Main Purpose: Orthotics are used to support, align, prevent, or correct deformities and improve the function of existing body parts.
Key Differences Between Prosthetics and Orthotics
- Purpose:Prosthetics: Replace a missing or amputated body part.
- Orthotics: Support or enhance the function of an existing body part.
- Function:Prosthetics: Aim to restore function, such as walking, grasping, or bending, by mimicking the missing limb or part.
- Orthotics: Focus on providing stability, correcting alignment, or alleviating pain in the body part being supported.
- Customization:Prosthetics: Highly customized to the individual’s anatomy to replicate the function and appearance of the missing limb.
- Orthotics: Often customized but focus more on fit and function to correct biomechanical issues.
- Materials:Prosthetics: Can include advanced materials such as carbon fiber, titanium, and robotics for added function and durability.
- Orthotics: Often made from lightweight materials like plastic, foam, or metal to provide structural support.
- Users:Prosthetics: Typically used by individuals who have undergone amputation or were born without a limb.
- Orthotics: Used by people who require extra support for existing limbs or joints, often for rehabilitation, injury prevention, or correcting long-term conditions.
Applications in Daily Life
- Prosthetics: Help users regain independence by allowing them to perform daily tasks like walking, running, lifting, and grasping. They are vital in allowing individuals to return to work, sports, or hobbies.
- Orthotics: Provide relief for conditions such as arthritis, cerebral palsy, stroke recovery, or sports injuries. They support proper alignment and reduce pain, enabling individuals to stay active and maintain a healthy lifestyle.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Solution
Both prosthetics and orthotics play a critical role in helping individuals overcome physical challenges, but they serve very different needs. Prosthetics replace lost limbs and restore functionality, while orthotics support and enhance the function of existing body parts. The choice between a prosthetic or an orthotic depends on the nature of the individual’s condition, their physical needs, and their rehabilitation goals. Healthcare professionals work closely with patients to evaluate and recommend the best solution for each individual, ensuring the highest quality of life possible.